Special Symbols
The following special symbols are used in Thai writing.
ๆ Repetition
The repetition character indicates a repetition of the previous word.
Repeated words are often used to add emphasis or intensify the meaning.
The repetition character itself is called
ยมก 
/ya
H mohk
H/.
ฯ Abbreviation
This appears most famously in the
Thai name of the capitol city which Westerners call Bangkok. The
actual name of the city, the longest place name in the world, is:
กรุงเทพมหานครอมรรัตนโกสินทร์มหินรายุธยามหาดิลกภพนพรัตนราชธานีบูรีรมย์อุดมราชนิเวศมหาสถานอมรพิมานอวตารสถิตสักกทัตติยะวิษณุกรรมประสิทธึ์  |
groongM thaehpF maH haaR naH khaawnM aL maawnM ratH dtaL naH go:hM sinR thaH maH hinR thaH raaM yootH thaH yaaM maH haaR diL lohkH phohpH nohpH phaH ratH raatF chaH thaaM neeM booL reeM rohmM ooL dohmM raatF chaH niH waehtF maH haaR saL thaanR aL maawnM phiH maanM aL waH dtaanM saL thitL sakL gaL thatH dtiL yaH witH saL nooH gamM bpraL sitL
|
Great city of angels, supreme repository of divine gems, great
unconquerable land, grand and prominent realm, royal and
delightful capital city full of nine noble gems, highest royal
residence and grand palace, divine shelter and home of
the reincarnated spirits. |
Using the abbreviation symbol, the name is commonly abbreviated as follows:
กรุงเทพ 
/groong
M thaehp
F/.
This symbol is called
เปยยาลน้อย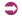

/bpeeuy
M yaan
M naawy
H/.
ฯลฯ Et cetera
This symbol is called
เปยยาลใหญ่

/bpeeuy
M yaan
M yai
L/.
อ์ Silence
The silence character is placed over a consonant which is not pronounced. It is frequently used in loanwords (words borrowed from
another language and spelled phonemically with the Thai alphabet) to indicate that the original word had a letter which the Thai do not
pronounce. In the following example, each consonant ร carries the silence marker since there is no final /-r/
phoneme in Thai:
The silence mark itself is called
การันต์ 
/gaa
M ran
M/.
There are also a Thai few words in which the final consonant or vowel (or occasionally even a non final consonant) is silent although not marked with the gaaran; for example,
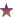 จักร
จักร 
/jak
L/ does not have a gaaran for the final consonant
ร. The vowel
อิ in
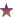 ญาติ
ญาติ 
/yaat
F/ is silent, so the the word should be
pronounced as shown, not "yaadti." This word also does not contain the gaaran to indicate that the final vowel is silent.
There are other special cases. For example, the
consonant cluster ทร is often treated as a single consonant, thus in the word
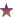 จันทร์
จันทร์ 
/jan
M/ the gaaran indicates that the last two consonants are both silent.
฿ Baht
The Thai currency symbol, used as a prefix on numeric
 บาท
บาท 
amounts.
๏ Paragraph
Known as
ฟองมัน

, or informally the "bird's eye"
ตาไก่

, this symbol can be used to indicate the beginning
of paragraphs, but is now used only for special poetic or artistic effect.
อฺ Phinthu (พินทุ  )
)
This archaic orthography is nowadays mostly used in dictionaries to disambiguate pronunciation. In our
online dictionary, the symbol, if used, only
appears in a word at the top of its main definition page. The symbol can be used in two ways:
- Placed underneath the first consonant of an orthographic consonant cluster which may in turn be one of three cases:
a. A double-consonant cluster
b. Silent ห, called หอ นำ
 /haawR namM/
/haawR namM/
c. Silent อ, called ออ นำ
 /aawM namM/
/aawM namM/
- Placed underneath the final-sounding consonant of a syllable.
Both of these rules can be summarizied "more snappily," as Richard Wordingham says, by noting that "
Phinthu indicates that there is no vowel sound
associated with the [marked] consonant." These seemingly vague rules can be puzzling; for clarity, our online dictionary will only place
พินทุ 
/phin
M thoo
H/
under
ห or
อ when that consonant is acting in its silent role.
๚ อังคั่นคู่ /angM khanF khuuF/
/angM khanF khuuF/
Indicating the end of a chapter, episode, verse, or section of Thai text.
๚
๛ Khomut (โคมูตร
 ) The End
) The End
Used to mark the end of the entire text.
๚ะ๛


 /yaH mohkH/.
/yaH mohkH/.
 /groongM thaehpF/.
/groongM thaehpF/.
 /bpeeuyM yaanM naawyH/.
/bpeeuyM yaanM naawyH/.

 /bpeeuyM yaanM yaiL/.
/bpeeuyM yaanM yaiL/.
 /gaaM ranM/.
/gaaM ranM/.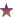 จักร
จักร  /jakL/ does not have a gaaran for the final consonant ร. The vowel อิ in
/jakL/ does not have a gaaran for the final consonant ร. The vowel อิ in 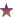 ญาติ
ญาติ  /yaatF/ is silent, so the the word should be
pronounced as shown, not "yaadti." This word also does not contain the gaaran to indicate that the final vowel is silent.
/yaatF/ is silent, so the the word should be
pronounced as shown, not "yaadti." This word also does not contain the gaaran to indicate that the final vowel is silent.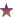 จันทร์
จันทร์  /janM/ the gaaran indicates that the last two consonants are both silent.
/janM/ the gaaran indicates that the last two consonants are both silent.
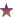 บาท
บาท  amounts.
amounts.

 , or informally the "bird's eye" ตาไก่
, or informally the "bird's eye" ตาไก่
 , this symbol can be used to indicate the beginning
of paragraphs, but is now used only for special poetic or artistic effect.
, this symbol can be used to indicate the beginning
of paragraphs, but is now used only for special poetic or artistic effect.
 )
)
 /haawR namM/
/haawR namM/
 /aawM namM/
/aawM namM/ /phinM thooH/
under ห or อ when that consonant is acting in its silent role.
/phinM thooH/
under ห or อ when that consonant is acting in its silent role.